A powerful biofield in a person is easy to determine by the following signs: Absence ...


FICUS BENJAMINA(F. benjamina) - decorative and deciduous evergreen plant of the Mulberry family. Widely used in indoor landscaping, can perfectly decorate any room or office, blending seamlessly with most styles.
The name of this type of ficus comes from the word benzoin, meaning benzoin resin, which the tree secretes. It is known that the ficus is a tree-symbol of Bangkok.
The Mulberry family includes about 1000 varieties of ficuses, of which Benjamin's ficus (F. benjamina) is more popular. The leader in the number of varieties with small leaves of different sizes, smooth and wavy edges, straight and twisted leaf blade, mono and variegated. The branches of Ficus Benjamin droop, which gives the plant a certain special appeal. The tip of each leaf is retracted and forms a dropper for draining excess water that falls on the leathery leaves.
The homeland of the plant is the tropical rainforests of Asia, where ficus grows at the foot of the mountains. In nature, it is evergreen tree reaching a height of 15-20 meters. V room conditions ficus Benjamin has a more modest size and with good care grows up to 2 meters in height. The lush and graceful crown of the ficus is formed by thin falling shoots strewn with numerous oval leaves. The bark of the trunk and branches is gray and smooth, with occasional brownish streaks. The leaves are 4-10 cm long and 2-5 cm wide, alternate, oblong-oval, with a retracted and pointed apex, thin, smooth, leathery. The color of the leaves is green with a glossy tint. Margins entire, veins reticulate, poorly visible. The length of the petiole is about 2 cm. Ficuses form fruits - syconia - oblong or round, orange or red.
Benjamin's ficuses in their genus are divided into varieties (Danielle, Exotica, Naomi, Wiandi), which differ in larger or smaller leaf sizes and their color (variegated or plain, with straight or wavy edges). Varieties of ficus Benjamin - Nuda, Hawaii, Natasha, variegata, Starlight, Gold Princes, in shape resemble a weeping tree up to 2 m tall. The difference is only in the shape of the leaves and color. For example, the form f. Benjamin Baroque leaf blades twisted in a spiral. Variegated varieties are the best.
 Today, this evergreen small tree or shrub is becoming increasingly popular due to its rapid growth and easy care.
Today, this evergreen small tree or shrub is becoming increasingly popular due to its rapid growth and easy care.
The optimum temperature of the content is 20-25 degrees. From the first days of the appearance of ficus indoors, it needs to provide a permanent location, protected from drafts and direct sunlight. You should not often move and move the flowerpot with a flower, otherwise it will lead to foliage falling off on one side. He will be quite normal near a shady window or near a south sunny window at a short distance. Variegated varieties of ficus Benjamin are recommended to be placed in a more lit place so that the peculiar color of the leaves does not disappear.
- Watering and humidity.
Watering should be regular and moderate: in summer 2-3 times a week, in winter - no more than once a week. The soil should not be allowed to dry out. The soil should be slightly damp before the next watering. In order for the soil to dry evenly, it must be loosened once every two weeks. Water for irrigation and spraying should be settled (at least 12 hours), soft, at room temperature.
Spraying is beneficial for ficuses all year round: in summer in hot weather twice a week, in winter - once a week. The plant does not tolerate dry air, it should not be placed near heating systems, otherwise the tree may react with yellowing and dropping foliage.
- Ficus transplant.
A young plant is transplanted in the spring every year by transshipment, into a container 2-3 cm larger in diameter, a mature plant - once every two to three years. Once a year, you can renew the topsoil by 3-5 cm, if it has formed white coating- salt crust. The composition of the substrate is formed from the following components: leaf and peat soil in a ratio of 2:1.
It is not recommended to transplant Benjamin's ficus into large pots, except when the roots are completely covered with an earthen ball. Signs that the plant needs a transplant when the container has become cramped with ficus, rapid drying of the soil after watering, roots coming out of the drainage holes.
Within a few weeks after transplantation, the plant may drop leaves, ficus growth may slow down, as root system takes some time to adapt. Then everything should return to normal ... It is necessary to continue to spray and water the plant correctly and after a short time young leaves will appear, and the ficus will adapt to new conditions.
- fertilizers.
Since Benjamin's ficus is growing rapidly, the soil for it must be constantly fed. In the spring, as soon as young leaves begin to appear on the ficus, the soil can be fertilized. Top dressing is carried out all summer (from March to September) once or twice a month, and is stopped in the fall. Suitable liquid universal fertilizer for decorative indoor flowers with a high nitrogen content for the development of green mass. Before the introduction of fertilizer, the plant should be well watered so as not to burn the roots. For ficus, not only root top dressing is recommended. Spraying the foliage with a weak solution of fertilizers has a beneficial effect.
V winter time ficus is not fertilized, since vegetation is undesirable during this period due to lack of light, heat and moisture. Stimulation to growth leads to the formation of weak and elongated shoots. Well, in the case of using artificial lighting and providing optimal humidity air, ficuses are fed once every 1-2 months with a weak solution of fertilizer (1/2 of the usual dose), with a low nitrogen content, so that the plant does not grow with a lack of light.
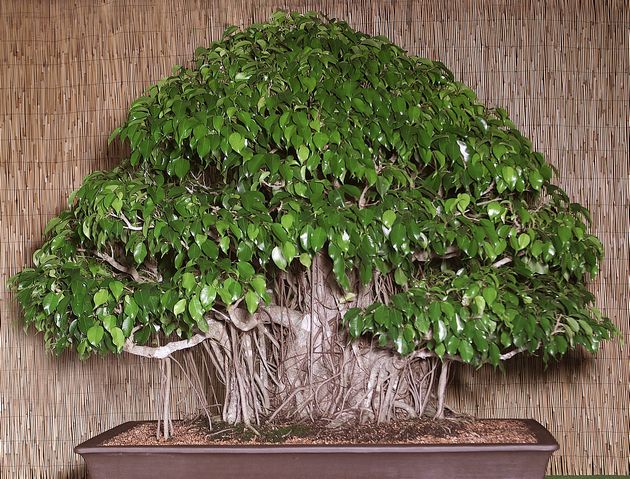
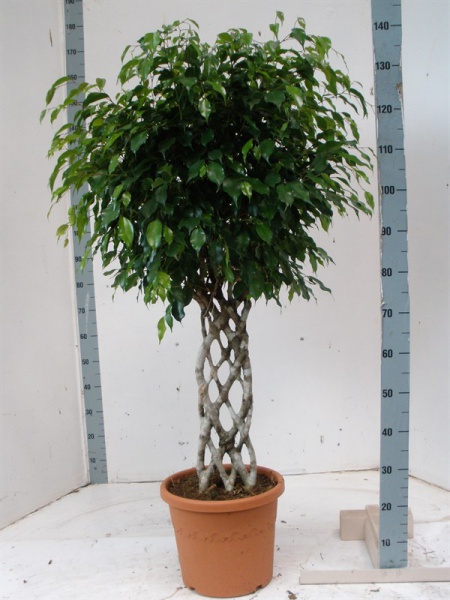
To give a decorative shape to a tree, you can plant two or three plants in a flowerpot. Sometimes trunks, due to their flexibility in young age, are woven into a pigtail, which allows you to create an unusual lush crown. Formation in the form of a bush, one- or multi-tiered trunk, sculptures various forms, in bonsai style. The active development of the root system has to be restrained by cramped pots and pruning ...
You should not be afraid if, in the first weeks of being indoors, the ficus begins to partially shed its foliage. Thus, the tree reacts to changing conditions environment. Quite naturally, ficus leaves fall in the process of growth and renewal. In winter, Benjamin's ficus can also lose some of its foliage (up to 30%), which is a normal process.
But when the crown thins before our eyes, amateur flower growers are often lost, not knowing what to do and how to help their plant. Most often, this phenomenon is caused by insufficient watering, drafts or temperature changes. If the plant is moved in a timely manner, creating it comfortable conditions, the drying and falling of the leaves will stop. Lighting, temperature and humidity are in direct proportion ...
Periodically, the ficus can be shaken, dry and falling leaves can be removed, thereby releasing it in a timely manner and providing air access to dense foliage. More details about this problem are described on a separate page at the link below...
Mulberry family. Ficus benjamin - one of the most common indoor plants. In nature, it grows in India, China, South Asia, as well as the Philippines, Hawaii, and Australia.
These are evergreen shrubs and trees. In nature, they grow like our birches, about 20-25 meters in height, at home, Benjamin's ficus does not grow quickly and in about 10 years it will reach 100-120 centimeters in height. Ficus has an invasive root system that spreads not only in depth, but also on the surface of the earth, aerial roots old plants growing in a humid tropical climate form entire arrays of supports under a wide spreading crown. At indoor ficuses in pots, the root system is quite strong, the roots over time, if you do not sprinkle the earth, are shown above the surface of the earth, but aerial roots do not form.
Ficus benjamin has a dark gray bark, with brown transverse strokes. It branches very well, the shoots are drooping, the leaves are alternate, on short petioles, smooth, shiny, leathery, oblong (elliptical) or lanceolate, pointed at the end, 6-12 centimeters long and 3-6 centimeters wide. The fruits are siconia, about 1.5 cm in diameter, paired, axillary, red, burgundy when ripe, inedible. Under room conditions, ficus benjamin does not bloom and, accordingly, does not bear fruit. At the break of the petiole, when the leaf is cut, the roots are pruned, a sticky white milky juice is released.
Ficus benjamin bred many varieties that differ in shape, size and leaf color:
Ficus benjamina variety Safari "Safari"
Small-leaved, leaves about 3-4 centimeters long, slightly bent like a boat along the central vein, the tip is only slightly bent. The leaves are marbled in color: dark green with wide and frequent cream strokes and spots. Grows slowly. With a lack of light, it quickly loses its variegation.
 Ficus benjamin grade Baroque "Barok"
Ficus benjamin grade Baroque "Barok"
The leaves are medium (about 4-6 centimeters), the length is 3 times greater than the width. The leaf is bent in a ring along the central vein. It grows slowly, branches weakly, several cuttings are planted in a pot to get a lush bush.
 Ficus benjamin grade Naomi Gold "Naomy Gold"
Ficus benjamin grade Naomi Gold "Naomy Gold"
The leaves are large (about 6-7 centimeters), the length of the leaf is 2-3 times greater than the width. The edge of the leaf is slightly wavy, practically not bent, the shoots are thin, drooping, the bark is light. In the photo, the variegated form of this variety, the simple "Naomy" leaves are dark green and differ from the "Monique" variety in the shape of the leaf - it is wider (not so elongated).
 Ficus benjamin grade Kinky "Kinky"
Ficus benjamin grade Kinky "Kinky"
Small-leaved, the length of the leaf (about 4 centimeters) is 2-3 times greater than the width. The leaves are straight, light green, cream or light green along the edge. Growth is moderate.
 Ficus benjamin grade Starlight "Starlight"
Ficus benjamin grade Starlight "Starlight"
The leaves are medium (about 4-6 centimeters), the length is 3 times greater than the width. The leaves are slightly bent in a boat along the central vein, the tip is only slightly bent, the edge is not wavy. The color of the leaves is deep green with a wide white stripe along the edge, some leaves are almost white. Grows fast.
 Ficus benjamin grade Natasha "Natasja"
Ficus benjamin grade Natasha "Natasja"
Small-leaved, the length of the leaf (about 3 centimeters) is 3-4 times greater than the width. The leaves are slightly bent in a boat along the central vein, the tip is only slightly bent, the edge is not wavy. Grows slowly.
 Ficus benjamin grade Nicole "Nicole"
Ficus benjamin grade Nicole "Nicole"
Small-leaved, the length of the leaf (about 4 centimeters) is 3-4 times greater than the width. The leaves are slightly bent in a boat along the central vein, the edge is not wavy. The trunk is slightly zigzag (like Wiandi), the shoots are directed upwards. The leaves are light green with a wide cream border. Growth is moderate.
 Ficus benjamin grade Monique "Monique"
Ficus benjamin grade Monique "Monique"
The leaves are large, the length of the leaf is 3-4 times greater than the width. The edge of the leaf is wavy, practically not bent, the shoots are thin, drooping. A variegated form with light green spots is also common. Grows pretty fast.
 Ficus benjamin variety Wendy "Wiandi"
Ficus benjamin variety Wendy "Wiandi"
Small-leaved, the length of the leaf (about 3 centimeters) is 3-4 times greater than the width. The leaves are bent in a boat along the central vein, the tip is slightly bent. The trunk is zigzag, has many creases - a change in the direction of growth, fragile. Grows slowly.
 Ficus benjamin grade Eldorado "Eldorado"
Ficus benjamin grade Eldorado "Eldorado"
Very similar to the "Safari" variety, the difference is that Eldorado has larger leaves and wider ones. Leaves 5-6 centimeters long, twice narrower. Growth is moderate or fast.
 Ficus benjamin variety Carly "Curly"
Ficus benjamin variety Carly "Curly"
The leaves are medium, about 4-6 centimeters long, twice narrower, with a wavy edge, the tip is slightly bent. The leaves are dark green with white spots, different size(from large to small speckles) usually from the petiole and base of the leaf, some shoots grow with completely white leaves. With a lack of light, the color is lost. Grows slowly.
 Ficus benjamin variety Twilait "Twilait"
Ficus benjamin variety Twilait "Twilait"
The variety is very similar to Starlight - rich or dark green leaves with a white border, but unlike Starlight, the border is narrower.
Moderate, optimal for growth within 20-25 ° C, but by and large, the temperature of ficus benjamin is unimportant, but it is important that watering matches the temperature - water more often when it is hot and less often when it is cooler. In cool conditions, a wet earthen ball dries slowly, for a long time, and this is very harmful to the ficus. In winter, ideally, the temperature should be 16-18°C, with limited watering, a limit of 8-10°C when kept dry. But usually benjamin's ficuses grow well in normal home conditions, in heated rooms. If there is little light, the plants partially lose their leaves, so during a warm wintering, ficuses, especially variegated varieties, can be illuminated.
Ficus benjamin grows well in a bright place, with protection from direct sunlight at noon. An east window is perfect, where the sun is in the morning or evening. Variegated forms need a lighter and warmer place than dark-leaved forms. Only varieties with dark green leaves can grow well on the north window, and the variegated varieties "Safari" or "Eldorado" need a western window to preserve color, or a place in close proximity to the south, it is already dark on the east.
Moderate, ficus does not like waterlogging of the soil, it must be well dried before the next watering. From waterlogging, ficus benjamin may begin to rot the roots, while the plant simultaneously throws off a large number of leaves that lose color, become pale green. Water for irrigation is desirable soft, room temperature.
From March to August, once every two to three weeks, you can feed ficus benjamin with fertilizers for decorative leafy plants.
Leaves can be sprayed, especially in summer in hot, dry weather, but benjamin's ficus can do without it, it tolerates the dry air of apartments well. But in order to wash off the dust from the leaves, you need to rinse the foliage of the ficus under a warm shower, while carefully protecting the soil from the water jet.
Transplantation is carried out annually in the spring, in fresh soil. Old specimens are transplanted less often, every 2-3 years, but you can add fresh fertile land every year. The soil for ficuses should be loose and nutritious. A suitable mixture is 2 parts leafy soil, 1 part peat soil, 1 part sand and 1 part well-decomposed compost. You can also use leafy soil in its pure form, ficuses grow well in universal soils from the store. Large, old specimens that are rarely transplanted need heavier and more nutritious soil - the main component is turf land 2 parts, leaf or greenhouse 1 part, you can add chopped pine bark, vermiculite and charcoal. Important condition- good drainage to the bottom of the pot, and the acidity of the soil should be slightly acidic, or close to neutral (pH 5.5-6.5). Ficus does not tolerate alkaline and too acidic substrates.
Pots can be both ceramic and clay, they should not be too spacious, but in diameter 2-3 fingers wider than the root ball, or the pot in which the plant was bought. If it seems to you that the pot has become small (the roots have appeared from the drainage hole), then Benjamin's ficus can be transplanted again over the summer. If the roots are not cut or torn, then it tolerates the transplant well. After transplanting, refrain from watering unless it is too hot for 2 days (if the house is very warm and dry, you can water a little and spray the leaves).
The easiest way to propagate ficus benjamin cuttings, they easily take root in water, in a bright place at almost any time of the year. Just cut any twigs you like about 13-15 cm long, remove the two lower leaves and put in a jar of clean water. To prevent the water from blooming, cover the jar with an opaque cloth. Growth promoters are not needed. Cuttings of this size already have a woody stem, but if you cut a couple of leaves with a still green stem, it will not take root. Benjamin's ficus does not reproduce with a leaf, and large branches with thick bark take root for an extremely long time.
If for some reason the plant has become bald in the lower part of the trunk, it is easier to re-root the crown. For this, not cuttings are used, but air layering:

On the trunk, the bark is cut and removed in the right place, a strip about 1 cm wide. The trunk in this place is wrapped with sphagnum moss soaked in water (it is fixed with a thread only for the convenience of photography)
 Air layering ficus benjamin
Air layering ficus benjamin
We cut the plastic cup along the walls into two halves (cut the bottom to half and make a hole along the diameter of the trunk) and fix it on the trunk, fastening it with tape. We fill up the earth and water it.
 Air layering ficus benjamin
Air layering ficus benjamin
It is advisable to use a transparent glass so that you can see the appearance of the roots. The earth in the cup should be watered regularly, it should not dry out. Roots on this cutting appeared after 3 weeks.
Ficus benjamin itself has a beautiful crown, many varieties do not require any special shaping. However, if the trunk of the ficus is bare, you can stimulate the formation of new shoots and leaves by pruning. To do this, you can cut off part of the shoots, in whole or in part, sometimes it is enough to pinch the tips of the lower branches so that new buds start to grow. Pruning should be done in spring - early summer. The younger the ficus tree, the easier it is to form pruning.
In addition to trimming and pinching, the crown of ficuses is formed by bending with wire (for the formation of bonsai and pre-bonsai). Ficus shoots are quite flexible, easy to bend, but the thin bark can crack or peel off the wire, so it is applied loosely and braided wire is used. There should be a gap between the wire and the stems of the ficus - after all, the plant grows, and the branches gain thickness, with a tight winding, the wire will eventually grow into the bark.
![]() Ficus Baroque is formed with wire, the flexible trunks of the ficus can be bent quite steeply, striving to achieve the chosen bonsai style.
Ficus Baroque is formed with wire, the flexible trunks of the ficus can be bent quite steeply, striving to achieve the chosen bonsai style.
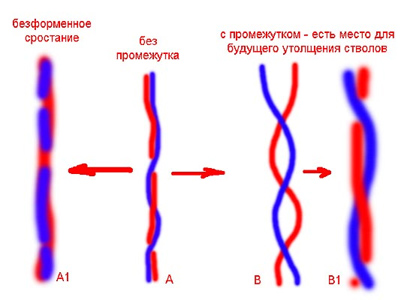 If you form a ficus by splicing with a trunk, then when braiding a pigtail of several trunks, be sure to leave gaps between them for the growth of the trunks in thickness. Drawing by Vitaly Alenkin.
If you form a ficus by splicing with a trunk, then when braiding a pigtail of several trunks, be sure to leave gaps between them for the growth of the trunks in thickness. Drawing by Vitaly Alenkin.
 Trunk splicing - several rooted cuttings are planted tightly to each other and wrapped with electrical tape. Part of the electrical tape has been removed and the fusion sites of the trunks are clearly visible. Further shaping is required.
Trunk splicing - several rooted cuttings are planted tightly to each other and wrapped with electrical tape. Part of the electrical tape has been removed and the fusion sites of the trunks are clearly visible. Further shaping is required.
Cuttings of some varieties of ficus benjamin branch reluctantly, single branches look and gain power slowly, can stretch upwards, even with sufficient lighting, begin to branch, reaching about 30-40 cm in height. Therefore, it is worth pinching, cutting the cuttings at a height of about 20 cm.
You can plant several cuttings in a pot, and if the stems are pressed tightly against each other, then for a very short term they grow together. You can bring the stems of ficus cuttings closer together using ordinary electrical tape - it is quite plastic and does not injure the bark, it stretches on growing trunks without growing. About once a month you need to inspect the braid, rewind if necessary. It is better, of course, to grow together trunks of small diameter, 5-7 mm, but thicker ones can also be spliced, only the process will take several years.
Another way to form is to twist the trunks with a pigtail or in the manner of a hedge - openwork weaving from the trunks of ficus benjamin. This method is only suitable for young flexible plants. At the same time, several large cuttings should be planted in one elongated container at a distance of 5 to 10 cm from each other strictly in a row. At first, each trunk grows vertically and forms a trunk (all lower branches are removed). Approximately at a height of 20-25 cm, ficuses can be fixed, tilted, crossing the trunks with each other. Fix with tape or jute.
The video shows how to wash off dust from ficus leaves, to prevent ticks. What to pay attention to when carrying out this procedure.
Ficus Benjamin is very common in the warm states of the USA, for example, in California, where it is grown as a hedge, in single or group plantings, in our country it is grown as a houseplant and greenhouse plant, in addition, it is very widely used in the bonsai style.
Very often there are questions about what affects the intensity of the variegated color of benjamin ficuses. There is no better way to express it than this explains it, so I will quote:
Variegated leaves do have areas containing chlorophyll (green spots) and areas without chlorophyll (white spots). Green, photosynthetic areas consist of chlorenchyma tissue, which includes chloroplasts - cells with a green pigment chlorophyll. These cells are involved in photosynthesis, i.e. With the help of carbon dioxide and water in the light, they synthesize the organic substances necessary for growth and development.
The white, non-photosynthetic areas are composed of cells lacking chloroplasts. In the leaf, these cells serve as accumulators. organic matter produced by chloroplasts.
A certain amount of light is required to create carbohydrate molecules. This molecule contains the necessary energy, which is subsequently spent by the plant on growth and development.
Thus, the ratio of white and green spots on variegated leaves directly depends on the conditions of the plant. The lack of light leads to a decrease in the synthesis of organic substances, and, consequently, the plant begins to "starve" and fight.
The consequence of such a struggle is the greening of the leaves in order to increase the chloroplasts and chlorenchyma, in general, for a greater synthesis of carbohydrate molecules!
The darker in the apartment, the more green the leaves will be and vice versa - the lighter, the brighter the pattern on the leaves will be.
And young leaves, just unfolded, stabilize their variegated color when they reach normal size. By this moment, the cells of young leaves receive information from the plant about its state (good and a lot of light, bad and little light) and it is already determined which tissue to form more - photosynthetic chlorenchyma or non-photosynthetic white spots.
Well, it remains to be added that if the young leaves have already turned green, they will not turn white. The white color to green during the development of the leaves may change, but the green color, back to white, does not.
As soon as you get a new ficus, you immediately want to know what variety it is and how to care for it. In fact, there are a great many varieties of ficus benjamin, many varieties with pure green leaves have variegated variegated forms, with spots, strokes different sizes and varying stability.
So, the ficus benjamin variety "Safari" is very unstable, the variegated marble color is easily lost if there is not enough sunlight, leaves with pure green leaves begin to grow. If the ficus pot is moved to a lighter place, shoots with variegated leaves begin to appear again.
But some other variegated varieties of Benjamins, for example, the Starlight variety, are more resistant to lack of light and even in light shading retain white spots on the leaves.
Different varieties of ficus benjamin differ in growth rates - some grow very slowly, growing several centimeters a year, with good conditions content, other varieties, for the same time double the increase.
Many varieties of ficuses are very similar to each other at first glance, some, even upon closer examination, raise doubts about the definition of the variety (for example, there is an opinion that the varieties "Safari" and "Eldorado" are two names of the same variety).
The differences are, first of all, in the shape of the leaf (in some varieties it is more elongated, the leaves are narrow; in others, the leaves are wider, oval); in the waviness of the edge (some literally have a corrugated edge, in other varieties - a slight, barely noticeable waviness, in others a pronounced waviness); the leaf plate can be straight along the central vein or bent in a boat, or, like in the Baroque variety, bent in a ring.
They also pay attention to the trunk - in many varieties it is straight, but in some it changes direction at the nodes, it becomes zigzag, as if broken. The direction of the shoots of most benjamin ficuses is first up, then they droop, and in such as the curly variety "Baroque" or "Nicole", the stems are directed upwards and do not droop.
Ficuses are photophilous, they need bright diffused light, with some direct sun, variegated varieties of sun rays are required. Dark-leaved ficuses can grow in light shade, but growth is greatly slowed down, and the crown will not be dense. Ficuses grow well under completely artificial lighting.

But even the most light-loving varieties of ficus, like Starlight, require shading during the hottest hours of the day in summer - on the southern and western windowsills. Use tulle or veil to create diffused light.
As for watering, the ficus should be watered only as needed, i.e. when the earthen ball in the pot dries well.
The leaves of the ficus are covered with a thin dense skin, which protects it much more reliably from strong evaporation of moisture than, for example, those of arrowroot. Therefore, water requirements are very small, even if we consider that ficuses have a rather large leaf mass.
The only exception to the rule is dwarf ficus, it does not tolerate overdrying of the soil; it has fibrous roots. But in ficus benjamin, nodules are formed on the roots that can store moisture.
Therefore, excessive watering often leads to illness or death of ficus benjamin. The bad thing is that the plant reacts to root decay with massive leaf fall, and it is rather difficult to dry thick roots, they dry slowly.
To save the plant, you need to get it out of the pot and dry the root system with old newspapers or rags (wrap the roots with them and press firmly). Often, mushroom mosquitoes become a signal of waterlogging of the earth in pots with ficuses. This means that the plants need to be dried.
To what extent does the ficus tolerate overdrying? You can dry the soil to the state: in the dust. Those. lump will be completely dry. Some varieties may begin to fall leaves. But if you immediately water, the leaf fall will stop.
Pests rarely infect ficuses. Can harm them thrips, ticks, mealybug and shield.
Of all the listed insects, the scab is the most common pest, but fortunately, it can be eliminated from other ficus insect pests, with the exception of the tick, with systemic fungicides - actara or confidor (the prepared solution is watered and the plants are sprayed at the same time).
To prevent a tick from starting on Benjamin, you can rinse it in the shower once every two weeks. hot water(very hot - for a hand barely tolerable). If the tick still appears, you can fight it with drugs such as Actellik, Fitoverm or the BI-58 biological product.

If you got a stalk of ficus benjamin, before putting it in water for rooting, wash the leaves with a sponge and soap suds. It is best to take baby or laundry soap, carefully wipe each sheet on both sides. Leave to lie down for 5 minutes. Rinse with clean water and let root.
If you are fond of floriculture or just want to pick up a plant that can enliven the interior of an office, room or private house, pay attention to Benjamin's ficus, which has become a real hit not only in indoor floriculture, but also phyto-design and landscaping.
Let's find out what is the secret of his popularity? The answer is very simple. Ficus Benjamin does not need continuous care, like some plants, but in order for its crown to acquire a beautiful juicy green color, it needs an abundant amount of non-directional sunlight.
With such unpretentious care, the plant grows quite quickly. Just imagine how your interior will liven up as soon as your wonderful green pet reaches its natural height, which reaches 2-3 meters!

Fresh air is what the plant also needs. Having protected it from weather influences and drafts, the tree can be taken out to the balcony or placed on the windowsill.
In the future, you should not worry about how the plant will survive the winter: having enough nourished by the sun and breathing fresh summer air, it will be quite comfortable at a temperature of about +17 ° C. Another thing is if you opt for Benjamin's variegated ficus. This species is more sensitive to cold, more demanding on the temperature of the content and high humidity air.

Don't forget to water! Ficus requires a lot of water, especially in summer and during the period of active growth, so in no case do not let the soil dry out. In autumn and winter - watering should be reduced, doing it sufficiently only once a week.
Remember! If the owner forgets to water the plant or waters it insufficiently, the ficus, as if in retaliation, immediately sheds its leaves. But still, it is best to adhere to a reasonable balance when watering.
Having survived the winter, in the spring-summer period, the plant, like a person, becomes a little lethargic and especially needs to be fed. By feeding your indoor tree with a mineral complex fertilizer every two weeks, you can quickly reanimate it.

Inevitably, the time will come when the young ficus will become crowded in the former monastery and a transplant will be required. It needs to be dealt with in the spring, until the ficus fully grows, having bought a special soil or creating it yourself, mixing one part of leafy soil, grassroots peat, sand and two parts of soddy land. If, say, you already have a plant, then to create a comfortable living environment for an adult tree, it will be enough to update the topsoil.
pruning

In order for the trunk to acquire thickness and texture, experienced florists plant 2-3 plants together and twist their trunks into a tourniquet or pigtail, which over time takes on the appearance of beautiful bumpy growths.
If you beginner florist, we offer to start practicing in pruning the young Benjamin. To do this, on well-branched leaves, you need to cut off the top with 2-3 buds, and to maintain beautiful shape, repeat the procedure every 3-4 years, sprinkling sections with charcoal to prevent leakage of the milky liquid.
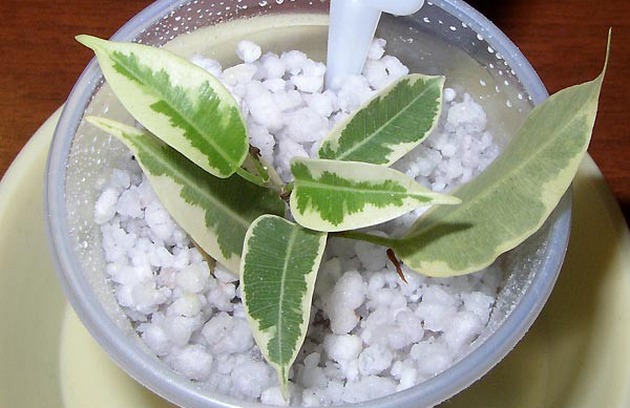

Ficus Benjamin is propagated by cuttings. To get its seedling, you can use leaves previously cut from the top or carefully cut off a new process. After that, the stalk can be wrapped in a thin cotton swab and put in water. After the plant takes root, plant in the ground or sand and irrigate regularly with water, waiting for it to rise.
ficus benjamina- one of the most popular decorative leafy houseplants. his homeland South Asia, Philippines, Australia. In nature, this is a large bush or tree, reaching a height of 8 - 10 m, in room conditions it grows up to 1.5-2 meters. The trunk is gray with small strokes. Branches inclined downward. Leaves on small petioles 2-2.5 cm, leaf blade oval with an elongated tip 4-8 cm long and 1.5-4 cm wide. The central vein is not clearly expressed. The sheet is dense, glossy. The color of the leaves varies from light green to very dark, there are many variegated forms.
ficus benjamin has great amount varieties differing in leaf size and variegation.
Variety "Daniel"- differs in very dark monophonic leaves.

Variety "Monique"- has more delicate, thin branches and a light, slightly wavy leaf along the edge.

Variety "Nicole"- has a more elongated sheet with a light edge.

Variety "Safari"- differs in obvious spotting and tricolor coloring.
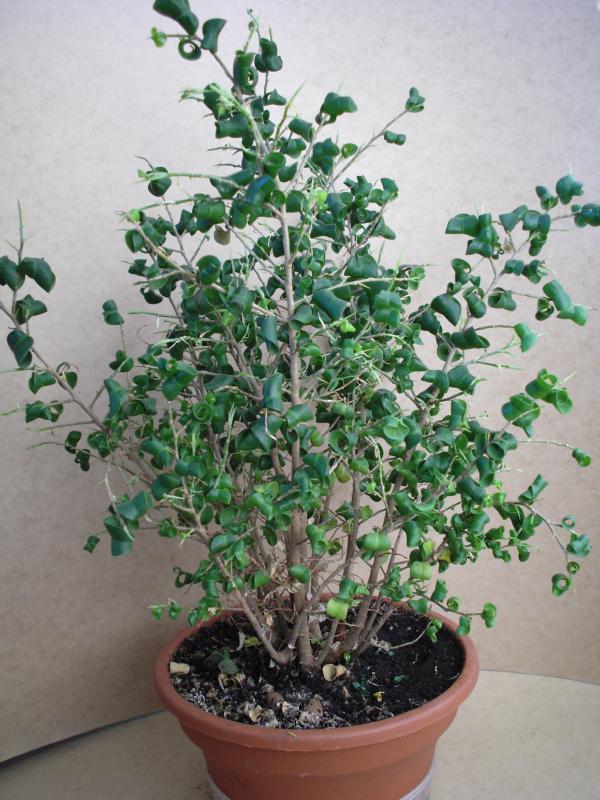

Variety "Baroque"- the most unusual and difficult to grow. Each leaf of this miniature plant twisted into a spiral.
Prefers bright, but not sunny places. In summer, it needs shading from direct sunlight, which can cause burns on the leaves. Required amount lighting also depends on the variegation of the leaves - the more variegated, the more light the plant needs. If the ficus is in the back of the room, it needs to be provided with additional illumination with a fluorescent or phytolamp. It is desirable that the backlight be directly above the growth point, in which case the crown will be more symmetrical.
The plant does not tolerate drafts and responds to them by dropping leaves.
For the summer, ficus benjamen can be taken out to the balcony or garden in a place protected from wind and direct sunlight. However, in this case, after bringing the ficus into the room, due to sudden changes in the conditions of detention, it will shed some of the leaves.
Prefers a temperature range of 20-25 ° C, in winter not lower than 15 ° C. Provided proper watering tolerate higher temperatures. Lowering the temperature below 15 °C will lead to mass leaf fall, and the temperature below 10 °C can lead to the death of the plant.
If the temperature in the room drops and it is not possible to transfer the ficus to a warmer room, the clod of earth should be well insulated. While maintaining the temperature of the roots, the ficus is able to tolerate lower temperatures for some time.
The plant should not be placed near heating appliances.
Water moderately after the topsoil dries out. The plant reacts to overdrying by dropping part of the leaves, from overflowing the leaves become light and the roots can rot. In winter, with a cooler content, watering is slightly reduced.
Watering is done with warm settled water. The water is drained from the pan.
For more intensive growth, it is advisable to regularly spray with warm boiled or filtered water. However, the plant grows well without spraying, easily adapting to the conditions of the apartment.
Only in winter in hot apartments with central heating foliar spraying is desirable to avoid loss of part of the leaves.
From time to time, it is advisable to wash the ficus in the shower to wash off the dust from the leaves. If the size of the crown allows, the crown can be completely immersed in water for a few minutes.
From spring to autumn, ficus is fertilized with universal fertilizers for decorative leafy plants, diluted in a slightly lower concentration than indicated on the package.
In winter, with a cool content, top dressing is stopped; with a warm content, they are fertilized once a month with fertilizers diluted in an even lower concentration.
Fertilizers are added to the water for irrigation and watered over the already wet coma of the earth.
The plant responds well to Epin treatment, which stimulates faster crown growth.
Young specimens are usually transplanted once a year in the spring, adults - once every 2-3 years, when the roots entwine the entire clod of earth. V large plants it is permissible to replace the top layer of the earth instead of transplanting.
Pots can be ceramic or plastic, a layer of drainage is needed. The size of the pot should be only 2-3 cm larger than the previous one.
Universal store soil is suitable for planting, or you can make a mixture of peat, leafy soil and sand in a ratio of 1: 2: 1.
Propagated by seeds, cuttings and air layering.
Growing problems:
Ficus benjamina is a fast growing plant that requires crown formation. If the plant is standing near a window, it is advisable to rotate it by 90 ° C every 2 weeks in order for the crown to grow evenly. But this is usually not enough. The plant needs annual spring pruning.

It easily tolerates pruning, which stimulates the formation of numerous side shoots. Pruning is usually done over a sleeping kidney, blotting the cut with a cloth and sprinkling it with charcoal. If the plant is small, you can pinch it - simply by removing the growing point.

From ficuses can be formed standard plants, removing the lower branches and forming a dense crown with pruning.

A very interesting effect can be achieved by intertwining the trunks of several plants. To do this, several young ficuses are planted and their trunks are intertwined. The bark is incised at the points of contact between the stems. As a result, plants grow quickly. In this way, you can form completely unusual openwork trunks.
"Shower" is very useful for those types of indoor flowers that love spraying: it washes dust from plants and gives them the opportunity to fully "breathe" (especially important on hot days), and is also good as a means of prevention and pest control. But it is advisable to cover the soil in a pot during the "shower" with cellophane: the plants are harmful to the tap water that has not been settled for at least a day, and pests washed off by the "shower" can get on the soil. Water the plants moderately after the "shower", the soil should be moist, but not wet, so that there is no stagnation of moisture in the pots. How often to arrange a "shower" for plants, temperature and other conditions will tell.
In the summer they need high humidity air (and mandatory spraying of the crown with water), in winter - normal. The temperature of the content of ficus Benjamin in winter should not be below 14 degrees; warm ground is essential.
It is necessary to protect Benjamin's ficuses from excessive watering, drafts, sudden changes in temperature, cold in winter and a significant change in conditions of detention - they can drop leaves. Benjamin ficus care.
ficus benjamina(F. benjamina) - shrub with thin drooping shoots and numerous elongated oval dark green leaves; can also grow to the ceiling. Large specimens develop aerial prop roots. There are several variegated varieties, especially beautiful "Hawaii" with small leaves, decorated with pure white spots.
Ficus Benjamin, blunt ficus (F. retusa), deltoid ficus (F. deltoidea) are widely used in room culture "bonsai" - dwarf trees. Of the curly and ampelous forms for rooms, the following are used: rooting ficus (F. radicans) with elongated leaves and creeping ficus (F. repens) with rounded leaves. Particularly attractive are miniature species: small-leaved ficus (F. pumila) and ivy ficus (F. hederacea), used as ground cover plants in miniature compositions. Showy types of ficuses are grown in room culture: with almost triangular leaves and copper-red shoots (F. buxifolia), white-spotted (F. sagittata), with black-red leaves (F. rubiginosa), etc.
All types of ficuses love a bright, but not sunny location, regular watering (moderate in spring and summer, limited in autumn and winter), wet air and frequent spraying. Between watering ficuses, you need to let the soil dry out a little (avoiding drying out the earthen coma), otherwise the leaves will fall off from stagnant moisture. With dry air and lack of light, ficuses can also lose leaves; species with green leaves are more shade-tolerant, variegated species are more photophilous. Most ficuses grow all year round at room temperature; for ficuses with green leaves in winter, the temperature may drop to 16 degrees (warm soil is important, hypothermia of the soil leads to dropping leaves). Ficuses need to be protected from drafts and cold air - two more causes of leaf loss.
If necessary, ficuses are transplanted in the spring (young plants annually, older than 5 years - after 2 years, old tubs - after 3-4 years). The substrate is made up of equal parts of compost or humus, sod, peat soil and sand; for large woody specimens, the proportion of sod land is increased). In summer, ficuses need to be fed with mineral and organic fertilizers(alternately 1 time in 2 weeks). Pruning shoots in most types of ficuses leads to branching. All ficuses reproduce by semi-lignified cuttings - the milky juice is washed off the cuttings and rooted in sand or in water at a temperature of 25-30 degrees.
When the air is too dry, pests settle on ficuses: scale insects, mealybugs, spider mites, thrips.
2.
The recommended time for transplanting ficus Benjamin is from March to August, therefore, if the ficus does not grow in peat, but in nutrient soil, it is better to postpone the transplant until spring. If the pot is too small, then you can transfer the ficus into a slightly larger pot with a drainage hole (3-4 cm larger in diameter and height): pour into new pot layer of drainage and nutrient substrate, carefully remove the earthen clod with roots from the old pot without damage and place it in a new pot, filling the space between the walls of the pot and the earthen clod with the substrate (with light tamping) and pouring a little on top.
Just collect the debris after pruning, dip in the root and stick into the wet substrate. V this case this is Ficus Benjamin, all other types and varieties of ficuses reproduce without problems by cuttings.
Reproduction by cuttings
The best time for this is spring and the first half of summer, when roots and leaves are actively formed. For rooting, it is better to take the tops of the shoots, especially from woody ones with large leaves - they make a slender plant faster. Species with creeping or clinging shoots ( ampelous plants), it is better to propagate by cuttings from the middle part of the stem. Then the dormant buds in the axils of the leaves wake up and start growing, and the shoot begins to branch. By planting only 2-3 rooted cuttings in a pot, after a while you can get a lush bush.
And no need to cut off long shoots, with in large numbers leaves, the evaporation of moisture is too great, and without roots, the stalk will quickly wither. It is better if there are 2-4 knots on the handle (the place where the leaf grows from). Sections are air-dried for 1-2 hours (this reduces the likelihood of decay) and then immersed in water or substrate. It is necessary to root the cutting in a warm, bright place, but not in the bright sun. Most houseplants easily root in water. For these purposes, settled tap water. If the stalk does not rot, then they do not change it, but only add fresh.
Cuttings with well-developed roots are planted in a small pot with a substrate and watered thoroughly. The next time watering is done only after making sure that the earth has dried up.
Tell us in more detail how to transplant and propagate ficus by cuttings and how to root them?
Transplantation (transshipment) of young ficuses is carried out in the spring every year, taking a slightly larger pot; an earthen ball with roots is removed from the old pot and transferred to a new one, pouring a fresh substrate from below, from the sides and a little from above. Ficuses older than 4-5 years are transplanted after 2 years, and large-sized old ficuses - after 3-4 years, but the deprived one is removed from the container annually. nutrients the top layer of soil and pour in a fresh substrate suitable for ficus.
For propagation of ficuses, spring and summer are most often used. apical cuttings with well-developed leaves, but segments of the middle part of young shoots are also suitable (about 7 cm long with 2-3 nodes - the lower oblique cut is made under the bud itself, the upper straight cut is 2 cm above the bud). The cuttings are cut with a sharp knife, the leaf is removed from the lower node and the cutting is lowered into tepid (25 degrees) water to stop the secretion of milky juice and prevent clogging of the cut. big leaves on the handle they are twisted into a tube with the bottom side inward and tied to reduce evaporation. The stalk is placed in a glass of water or planted obliquely in sand or a loose substrate, buried by one knot, and watered; For the stability of the handle, you can use a stick-support. The construction of a "mini-greenhouse" and a temperature of 25 degrees and above accelerate the rooting of the cuttings, which usually takes 3-4 weeks.
Rooting ficus cuttings in water is practiced in the warm season; as water is used up, fresh water is added to the glass. The stalk that has started roots is planted in a substrate and placed in a "mini-greenhouse" until a new leaf appears.
Ficus species with large leaves also propagate by short cuttings with a single node and leaf (cuts are made directly above and below the node); when planting, the stalk is slightly buried in the substrate so that the bud and the place of attachment of the leaf are on the surface of the substrate.
I don’t want to quote articles on caring for ficuses - I write as it is, without being smart
1. I plant in purchased soil for ficuses or palm trees, I mix the soil with vermiculite, about 20% vermiculite.
2. Drainage is mandatory, about 1/5th of the height of the pot. (purchased expanded clay)
3. I replant every 2 years in the spring (according to any need to replant - we water with tap water, so a lot of salts accumulate in the soil).
4. Fertilizers - no matter how fertilized - it grows, the infection. I fertilize with granular and dissolved fertilizers for ficuses, but somewhat unusual: in winter - concentrations as written in the instructions, once a month (November, December, January). From February to October, I make the concentration of fertilizers one third of that indicated on the package and add fertilizer with each watering. I try to buy different fertilizers - just like toothpaste.
When the plants are in large pots, 25-30 centimeters in diameter, planting in larger pots loses its relevance. Try removing the top few centimeters of soil by first loosening it with a fork. Replace it with a new one soil mixture the same type. This, combined with regular feeding, will allow many of the plants to grow in the same pot for many years.
5. All my ficuses grow on windowsills (western and eastern windows). In winter I try to light up.
6. I pinch, cut, bend the branches throughout the year. Tried to trim the leaves, results.
7. I always spray when I'm not too lazy - in the sense, it won't be superfluous. I always fill in the pulverizer hot water.
8. Watering - as needed - as soon as the top layer has dried up. ALWAYS WATER ONLY WARM WATER!!! The temperature of the water is about the same as for taking a bath.
9. Once a week during the growing season I spray with the drug.
10. Periodically I loosen the surface of the soil. (an ideal tool for this, and not only - cleaning the roots, for example - a regular toothpick).
11. Most a big problem in winter - low humidity in the room. Spraying saves literally a few minutes. There are two ways out: either buy a humidifier, or use SATURATOR . Scary word? and this is just a container of water suspended on a battery, standing on a battery, or a bowl of water under the battery. The device works like a clock, just add water.
12. Tools - watering can, sprayer. Perhaps everything. Next, toothpicks, scissors, a measuring cup from the first-aid kit, sharp knives, pieces of wire, a saw for metal are used - but this is in any apartment and you don’t need to buy it separately. Try to buy a watering can with a spray, such as in the shower, otherwise you will constantly bury holes in the pot, formed from water jets.
Helpful Hints:
1. One of the common indoor plants, ficus, often loses leaves. To prevent this from happening, do not keep the ficus warm. In a cool room, he will feel much better.
2. Water it only when the ground is dry. Its dryness can be determined by touch. Excess moisture can cause root rot and plant death.
3. When airing rooms in winter and in early spring leave the ficus away from the window, as a sharp, strong cooling can cause the leaves to fall.
If the ficus has lost its foliage, be sure to replant it in March. If the flower is very bare, cut off the top when transplanting and transplant. Side shoots will begin to appear at the trunk, and then the plant will take the form of a tree.
4. In winter (when radiators are working and the air is always dry in the apartment), ficuses are sprayed, and all plants are always there when they are. free time, in the morning and in the evening, on weekends sometimes several times. Drops on the leaves at night should not be left if your apartment is very humid, and the moisture from the leaves does not evaporate for a long time.
Remember to always spray with warm water!
5.Can be used hot shower for ficus. Such a procedure takes place, but it must be carried out according to certain rules:
A. Plants must be watered, this is a must. The best option- Water in the morning, take a hot shower in the evening.
B. The procedure is best done in the bathroom. Cover the substrate with polyethylene and water the plant from the shower for 10-20 seconds. The water temperature should be up to 45, maximum 50 degrees. In any case, check the temperature of the water on your hand.
C. After the procedure, we put the plant in a warm place, God forbid a draft.
A hot shower washes the plant well, cleanses it of pests, has a tempering effect and stimulates growth.
6. They brought me the shoots of ficus benjamin, its roots begin to grow, can it be planted now (in autumn) or is it better to leave it in the water until spring, and how to take care of it then .
If roots appear, plant Benjamin's ficus in the ground now, cover the planted cutting glass jar or build a "mini-greenhouse" over it in a pot, ventilate it every day and spray the stalk with water (you can add "Epin" to the water), and after the leaves dry, close it again with a jar - this will speed up the rooting of the ficus cuttings. On a light window sill, lay a warm cloth in a thick layer and place a pot of ficus on it (you can also wrap the pot with a cloth) so that the soil in the pot does not cool from the windowsill. After watering the ficus, drain the excess water from the pan and swaddle the pot again. Do not get carried away with watering the ficus - it should be moderate; The soil should dry out between waterings. From excessive watering, drafts or hypothermia, Benjamin's ficus loses its leaves.
Ficus benjamina (Ficus benjamina) belongs to the most widespread ficuses and to the most popular plants in landscaping, as it is very suitable for decorating a modern home and "fits" into most styles. This graceful ficus, growing 2 meters and above, has a lush crown of thin falling shoots, covered with an abundance of numerous oval leaves, and is very similar to a tree. Adult specimens develop aerial prop roots. The oval pointed leaves of ficus Benjamin, depending on the variety, are very small or wide (2-5 cm), short or very long (5-10 cm), brilliant green or variegated. The leaves of Ficus benjamina var.nuda have cream edges, while the leaves of 'Starlight' have white-mottled leaves. The small-leaved variety "Hawaii" is very beautiful, the leaves of which have pure white spots. Benjamin's variegated ficuses, in low light, lose their elegant color (their leaves turn green).
Ficus Benjamin is a very demanding plant and does not forgive mistakes. With good (sufficient lighting, moderate watering, regular spraying and, fresh air without drafts, etc.) Benjamin's ficus grows very quickly, actively branching and acquiring an abundance of leaves covering the branches. Timely and systematic formation of the crown allows you to get a lush dense tree. Young shoots of ficus Benjamin are very flexible, which allows young stems and branches planted next to each other in one pot, which gives an unusual decorative effect.
Ficus Benjamin is more than other types of ficuses, it looks like a tree with an abundance of thin hanging shoots. If, as Benjamin's ficus grows, the lower branches are regularly removed from the trunk, forming a tree with a bare trunk, and pinching the tips of long branches, stimulating the appearance of lateral shoots, then a very lush crown will form in the resulting standard ficus. The stems of Benjamin's ficuses, closely planted in one pot, are often intertwined ("tow" - two stems, "pigtail" - three stems), which creates a spectacular common trunk and combines the crowns of several plants into a single crown.
Compared to other plants, Benjamin's ficus is rarely affected by diseases and pests (scale insect, mealybug). However, if you do not let the soil dry out between waterings, the ficus roots suffer and begin. The same phenomenon is observed with errors in care, or when the tree is subjected to stress (long-term transportation, hypothermia of the substrate or crown, rearrangement to a new less favorable place, being in dark place, transplant, draft, etc.), and the reaction of the ficus to stress can be "late" for a month or more, when the troubles are long behind.
"Leaf fall" in ficus Benjamin manifests itself as a result of stress from transportation, hypothermia and other adverse effects (moreover, the leaves may not begin to crumble immediately, but sometimes a month after the stress) or errors in . Place the crown of the ficus in "", ventilate the greenhouse regularly and spray the crown with the addition of "Epin" according to the instructions. Between moderate waterings, let the soil dry out (otherwise the ficus roots will rot). Soon, young leaves will appear from sleeping buds on living branches; after that, dead branches without leaves can be cut off.
Ficus Benjamin - a fertile plant for "education" from his cuttings.
If you give this ficus favorable conditions for growth and learn to "understand" his needs, then Benjamin's ficus will live in the house for many years and become more and more beautiful and exotic.
Ficus flowers, without exception, do not tolerate drafts, waterlogging of the soil and direct sun (more light-loving ficuses are variegated forms that tolerate direct sun, but they also need shading during the hottest hours). Indoors, it is necessary to maintain air humidity and regularly spray the leaves, especially in summer.
Ficus care for which in winter requires sufficient illumination, in winter they are rearranged closer to the window. As for the variegated forms, for example, Benjamin's ficus, they can stand all winter on the south window at a temperature of at least 10 ° C. Due to the lack of lighting in winter, weak and twisted leaves and shoots can form.
Ficus, which is propagated by cuttings, can produce as many cuttings from its shoot as there are leaves on it. The propagating cutting should have one leaf with an intact eye and half of the lower internode without an eye. After cutting off the stalk, it is placed in warm water to stop the secretion of milky juice. In order for the cutting to take root better, a split or cut is made at the bottom of it, cross-shaped at the handle with hard wood, one cut at the handle with soft wood. Cuttings root better when covered with a plastic bag and with soil heating.
ficus plant does not like being planted in a container much larger than its root system, therefore it requires a transplant only when it fills the entire pot with its roots, usually in spring. ficus grows quite quickly, so the soil must be sufficiently nutritious. The optimal mixture consists of 2 parts of leafy soil and 1 part of peat and humus, from March to August it is good to saturate it with fertilizers. Upper layer earth is replaced when a white crust appears on it - a salt coating.
Visual changes in ficuses in diseases and improper care
The upper leaves remain elastic, but turn yellow. This is usually caused by a high calcium content in the soil - in those plants that cannot tolerate lime, or by hard water for irrigation.
Dots or spots on leaves. If the dots or spots are dry and brown, then the most likely cause is lack of water. If the affected areas are soft, dark brown in color, this is most likely due to waterlogging of the soil. If the dots or spots are white or yellowish, the lesion is caused by the use cold water when watering, water on the leaves, aerosol damage, too strong sunbeams or pest disease. If the affected areas are wet and blister-like, or dry and dented, the cause is disease. Some pests can also cause leaf spotting.
The leaves lose their luster and look lifeless. The likely cause is too much light; another cause could be a spider mite. Even healthy green leaves can look faded if left unwashed.
Brown tips or edges of leaves. The most likely reason for the drying of the tips of the leaves is dry air. Other possible reason- physical damage when the tips of the leaves are often touched or pressed against a window or wall. If the edges of the leaves are yellow or brown, this can be caused by several reasons: waterlogging of the soil, insufficient watering, lack of light, too much light, too low air temperature, too high air temperature, an excess of minerals, dry air or drafts. Other symptoms will help determine the true cause.
Leaves curl or fall off. This is a consequence of a lack of heat, waterlogging of the soil or damage by cold drafts.
The leaves suddenly fall off. Rapid leaf fall without previous long period wilting or color loss usually indicates a plant shock. It can be caused by a significant temperature difference (both cold and cold), a sharp increase in daylight intensity, or a strong cold draft. Sudden dropping of leaves, especially in tree-like plants, can also be caused by the drying of the soil at the roots.
Leaves turn yellow and fall off. lower leaves of an adult plant naturally turn yellow over time and then fall off. When this happens at the same time with several leaves, then the likely cause is waterlogging of the soil or cold drafts.
Drooping leaves. The usual causes are either drying out of the soil (due to insufficient watering) or waterlogging of the soil (due to poor drainage or too frequent watering). Other reasons may be too much light (especially if the leaves are drooping regularly in the middle of the day), dry air, too high an air temperature, a cramped pot, or pests.
Leaves fall on new plants. For newly transplanted, freshly bought, or transferred from one room to another plants, it is natural to lose one or two bottom leaves. The shock of a change of scenery can be alleviated by transplanting the plant into only a slightly larger pot than the previous one, covering it when moving it home from the store, and transferring it from a poorly lit place to bright light with a few days in partial shade in between.
The lower leaves dry up and fall off. Three probable causes - lack of light, too high air temperature and insufficient watering.
The plant grows slowly or does not grow at all. In winter, this is normal for all plants, so do not force it to grow. In summer, the most likely cause of growth retardation is a lack of minerals, waterlogging of the soil, or insufficient lighting. If these reasons are excluded, then, perhaps, the pot is cramped for the plant.
Variegated leaves become solid green. This is due simply to the lack of light. Remove all offshoots with the same color leaves (if possible) and move the plant pot closer to the window.
Leaves and stems rot. It is caused by a disease that occurs under bad conditions. Often the cause of the disease is waterlogging of the soil in winter or the ingress of water on the leaves, especially if it remains overnight.
Small pale leaves and elongated stems. This happens in winter and early spring, after the plant has been kept in low light conditions at too high a temperature and excessive watering. If possible, the ugly part of the plant is removed. If such symptoms appear during the growth period, then the reasons may be a lack of minerals or too poor lighting.
Torn edges and holes in the leaves. Most often they appear when they are physically damaged by pets or people (sometimes even a simple touch on an unfolded leaf can damage it) or when attacked by pests.
Green plaque on a ceramic pot. A sure sign of problems associated with watering - occurs when waterlogged soil or poor drainage.
White crust on a ceramic pot. Probable Causes two - the use of too hard water for irrigation or an excess of minerals.