INSTRUCTIONS AND PROPHECIES OF THE Blessed MOTHER ALIPIA GOLOSEEVSKY, Kyiv...

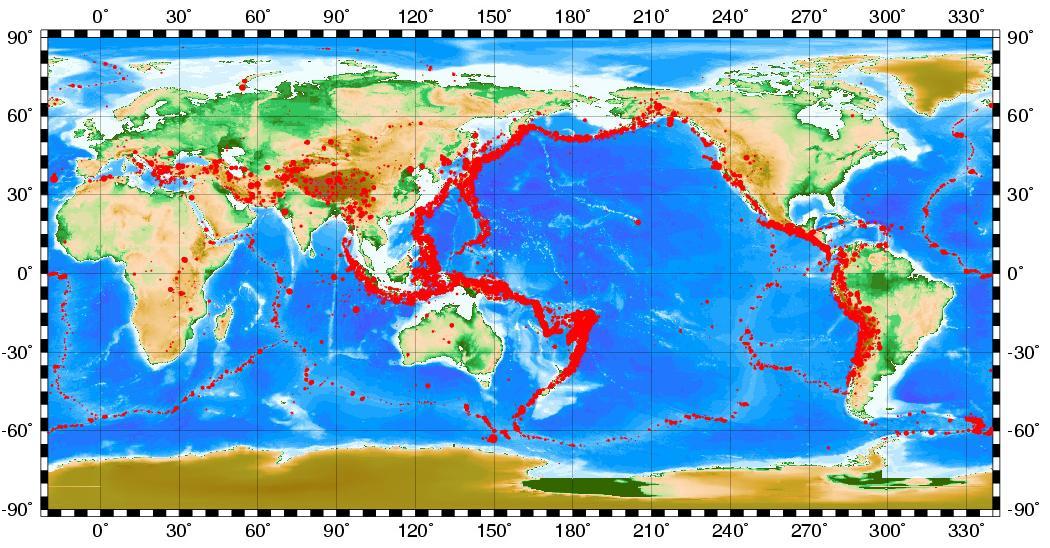
As earthquake statistics show, seismological disasters account for 13% of the total number of natural disasters. Over the past hundred years, about 2,000 aftershocks with a magnitude of 7 or more have occurred in the world. Of these, 65 cases exceeded the 8 mark.
If you look at the world map, on which seismological activity is displayed with dots, you can notice one pattern. These are some characteristic lines along which tremors are intensely recorded. These zones contain tectonic boundaries. earth's crust. As statistics have established, strong catastrophic earthquakes, entailing the most devastating consequences, occur due to stress in the focus of "grinding" of tectonic plates. 
Earthquake statistics for 100 years show that only on continental tectonic plates (not oceanic) about a hundred seismic catastrophes occurred, in which 1.4 million people died. In total, 130 strong earthquakes were recorded during this period.
The table shows the largest known seismic catastrophes since the 16th century:
| Year | Location of the incident | Destruction and casualties |
| 1556 | China | 830 thousand people became victims. According to current estimates, the earthquake can be assigned the highest score - 12 points. |
| 1755 | Lisbon (Portugal) | The city was completely destroyed, 100 thousand inhabitants died |
| 1906 | San Francisco (USA) | Most of the city was destroyed, 1,500 people became victims (7.8 points) |
| 1908 | Messina (Italy) | The destruction claimed 87 thousand human lives (magnitude 7.5) |
| 1948 | Ashgabat (Turkmenistan) | 175 thousand people died |
| 1960 | Chile | The largest earthquake recorded in the last century. He was rated 9.5 points. Three cities were destroyed. About 10 thousand inhabitants became victims |
| 1976 | Tien Shan (China) | Magnitude 8.2. 242 thousand people died |
| 1988 | Armenia | Several cities and towns were destroyed. More than 25 thousand victims recorded (7.3 points) |
| 1990 | Iran | About 50 thousand inhabitants died (magnitude 7.4) |
| 2004 | Indian Ocean | The epicenter of the earthquake 9.3 points was at the bottom of the ocean, formed claimed the lives of 250 thousand inhabitants |
| 2011 | Japan | An earthquake with a magnitude of 9.1 caused the death of more than 15 thousand people and caused enormous economic and environmental consequences not only for Japan, but for the whole world. |
Over 30 years of the end of the 20th century, about 1 million people died in seismic catastrophes. This is about 33 thousand per year. Over the past 10 years, earthquake statistics show an increase in the average annual figure to 45 thousand victims.  Hundreds of imperceptible oscillations of the earth's surface occur every day on the planet. This is not always associated with the movement of the earth's crust. Human actions: construction, mining, blasting - they all entail fluctuations recorded by modern seismographs every second. However, since 2009, the USGS Geological Survey, which collects data on earthquake statistics in the world, has ceased to take into account shocks below 4.5.
Hundreds of imperceptible oscillations of the earth's surface occur every day on the planet. This is not always associated with the movement of the earth's crust. Human actions: construction, mining, blasting - they all entail fluctuations recorded by modern seismographs every second. However, since 2009, the USGS Geological Survey, which collects data on earthquake statistics in the world, has ceased to take into account shocks below 4.5.
The island is located in a tectonic fault zone, so increased seismological activity there is a frequent phenomenon. Earthquakes in Crete, according to statistics, do not exceed 5 points. With such a force, there are no devastating consequences, and the locals do not pay attention to this shaking at all. On the graph, you can see the number of registered seismic shocks by month with a magnitude above 1 point. You can see what last years their intensity increased somewhat. 
The country is located in a zone of seismic activity on the territory of the same tectonic fault as Greece. Earthquake statistics in Italy over the past 5 years show an increase in the number of monthly shocks from 700 to 2000. In August 2016, a strong earthquake of magnitude 6.2 occurred. That day claimed the lives of 295 people, more than 400 were injured.
In January 2017, another earthquake of magnitude less than 6 took place in Italy, and there were almost no victims of the destruction. However, a push has caused in the province of Pescara. The hotel Rigopiano was buried under it, killing 30 people.
There are resources where earthquake statistics are displayed online. For example, the organization IRIS (USA), engaged in the collection, systematization, study and distribution of seismological data, presents a monitor of this type: 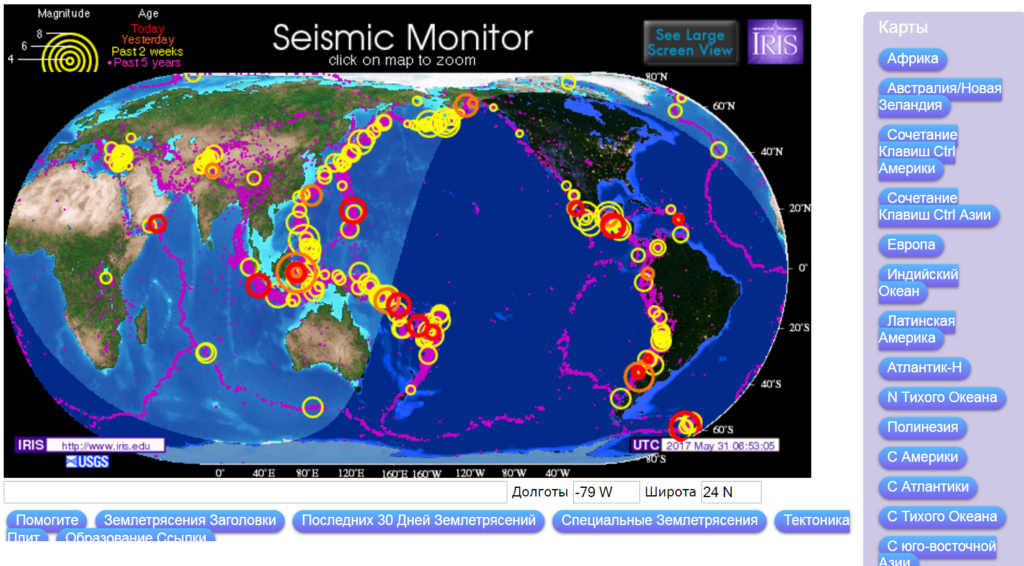 Information is available on the site that displays the presence of earthquakes on the planet in this moment. Here their magnitude is shown, there is information for yesterday, as well as events 2 weeks or 5 years ago. You can consider in more detail the parts of the planet of interest by selecting the appropriate map from the list.
Information is available on the site that displays the presence of earthquakes on the planet in this moment. Here their magnitude is shown, there is information for yesterday, as well as events 2 weeks or 5 years ago. You can consider in more detail the parts of the planet of interest by selecting the appropriate map from the list.
According to the statistics of earthquakes in Russia and the OSR (General Seismic Zoning) map, more than 26% of the area in the country is located in seismically hazardous zones. There may be shocks from 7 points. This includes Kamchatka, the Baikal region, the Kuriles, Altai, North Caucasus and Sayans. There are about 3,000 villages, about 100 thermal power plants and hydroelectric power stations, 5 nuclear power plants and enterprises of increased environmental danger.
There are about 28 districts of the region in the zone, of which there are approximately 4 million people. Among them is the large resort city of Sochi - according to earthquake statistics, the last seismic activity above 4 points was recorded in the fall of 2016. Kuban is mostly located in zone 8–10 ball earthquakes(MSK-64 scale). This is the highest seismic hazard index throughout the Russian Federation.
The reason is the resumption of tectonic processes in 1980. earthquake statistics in Krasnodar Territory annually registers about 250 seismic shocks of more than 2 points. Since 1973, 130 of them have been a strength of 4 points. Tremors with a magnitude of more than 6 points are recorded once every 5 years, and above 7 - once every 11 years. 
Due to its location near the Baikal Rift, Irkutsk's earthquake statistics record up to 40 minor shocks every month. In August 2008, seismic activity with a magnitude of 6.2 was recorded. The epicenter was in Lake Baikal, where the indicator reached 7 points. Some buildings cracked, but no significant damage or casualties were recorded. In February 2016, another earthquake of magnitude 5.5 occurred.
Even though the growth Ural mountains has long ceased, the statistics of earthquakes in Yekaterinburg continues to be replenished with new data. In 2015, a 4.2 magnitude shock was recorded there, no one was injured.
Between the end of 2008 and 2011, there was a decrease in seismic activity on the planet, to a level of less than 2,500 cases per month and a magnitude above 4.5. However, after the earthquake in Japan in 2011, in the period from 2011 to 2016, there is a tendency to increase the activity of tremors around the world by almost 2 times. Earthquake statistics for recent years are as follows:
 Predicting earthquakes is very difficult. Often you can say with certainty where it will happen, but when exactly it will happen is impossible to determine. However, there are biological precursors. the day before strong earthquake and other representatives of the fauna living in this territory begin to behave abnormally.
Predicting earthquakes is very difficult. Often you can say with certainty where it will happen, but when exactly it will happen is impossible to determine. However, there are biological precursors. the day before strong earthquake and other representatives of the fauna living in this territory begin to behave abnormally.
The greenhouse effect stumbled
Vladimir Erashov
In recent decades, the greenhouse effect has become a byword, it is blamed for the growth of all earthly cataclysms. But here's a sensational surprise - THE GROWTH OF THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT AND THE NUMBER OF EARTHQUAKES COMEDIATED ONLY UNTIL 2005, THEN THE WAYS DIFFERED, THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT CONTINUED TO GROW, THEN THE NUMBER OF EARTHQUAKES STARTED TO DECREASE SHARPLY. Moreover, the statistics of earthquakes is as follows, we will give it below, which leaves no doubt about the presence of the indicated trends. Until 2005, the number of earthquakes on Earth increased many times, and then it also began to decrease many times over. Earthquakes in the present times are recorded by many tracking stations with great accuracy and very scrupulously. From this side, any error is ruled out in principle. Consequently, the indicated trend is an indisputable fact, a fact that allows us to look at the problem of climate warming in a very unconventional way.
First, let's give the statistics of earthquakes, this statistics was obtained after processing (summing up) the daily number of earthquakes stored in the archive of the site http://www.moveinfo.ru/data/earth/earthquake/select
Let us clarify that the site stores earthquakes of magnitude four and above, starting from 1974. It has not been possible to process all the statistics yet, it is very laborious, we present the statistics of January earthquakes, for other months the picture is similar.
Here are the stats:
1974 -313, 1975-333, 1976 -539, 1977 – 323, 1978 – 329, 1979 – 325, 1980 – 390, 1981 -367, 1982- 405, 1983 – 507, 1984 – 391, 1985 – 447, 1986 – 496, 1987 – 466, 1988 – 490, 1989 – 490, 1990 – 437, 1991 – 516, 1992 – 465, 1993 – 477, 1994 – 460, 1995 – 709. 1996 – 865, 1997 – 647, 1998 – 747, 1999 – 666, 2000 – 615, 2001 – 692, 2002 – 815, 2003 – 691, 2004 – 915, 2005 – 2127, 2006 – 971, 2007 – 1390, 2008 – 1040, 2009 – 989, 2010 – 823, 2011 – 1211, 2012 – 999, 2013 – 687, 2014 – 468, 2015 – 479, 2016 – 499.
And so in 2005 there was a radical change in the number of recorded earthquakes, if until 2005 the number of earthquakes, albeit with small stops, only grew, then after 2005 it began to steadily decline.
Main conclusion:
The catastrophic increase in the number of earthquakes that occurred on Earth until 2005 with greenhouse effect not connected in any way, it occurred for other reasons, these reasons have yet to be clarified.
An interesting fact - in 2005, in parallel with the increase in the number of earthquakes, a radical change occurred in the speed of the Earth's rotation, the Earth began to slow down its rotation. Now it is impossible to unequivocally state that these facts are connected with each other, but it is also very unlikely that they coincided by chance. Moreover, short-term bursts in the number of earthquakes correlate very well with bursts in the speed of the Earth's rotation.
From the works of the scientist Sidorenkov N.S. It is known that the speed of the Earth's rotation has a very good correlation with the temperature on the Planet, a higher speed of the Earth's rotation corresponds to a higher average temperature - this has been established experimentally over a fairly long period of observations. Then a perfectly logical question:
Will the decrease in the speed of the Earth's rotation not only be followed by a decrease in the number of earthquakes, it has already followed, but also a decrease in average temperature, that is, do not these factors signal us about the beginning of the cooling era?
Apparently, it is too early to put an end to this issue, but Russian science has no right to leave this issue unattended, the stakes are too high. Of course, no scientist can cancel the future cooling of the climate, which may be about to begin, but this cooling should not fall on Russia like snow on its head.
In this regard, I ask readers not to be lazy, but to re-read the article “Transparent Climate”.
Isn't it time Russian science wake up?
24.05. 2016
And introduce you to a couple of wonderful services.
There are many seismically active regions on planet Earth, where tremors occur with a certain frequency. Their causes are overwhelmingly natural and due to the movements of tectonic plates. Despite the actively developing research in this area and good technical equipment, it is almost impossible to predict where and at what point on the planet tomorrow or today there will be an earthquake. It remains only to follow exactly where they occur ...
This map shows the most full information seismic activity from all major geological sources. You can change its scale by holding down the CTRL key and scrolling the mouse wheel, switch between display modes as a map or from a satellite:
The advantage of this map is that it collects specific numerical statistics in the form of graphs for tremors around the world:
And in the table, data is updated online (on top, the most recent) for all earthquakes in the world, indicating their characteristics and data source.
In the central part of the screen you see a display of our planet and circles representing the epicenters of seismic activity at the present time. In the left part of the window there is a monitor (constantly updated list) of the latest information:
By clicking on any event from the list in the pop-up window you will find more detailed information about it:

The size of the circles on the map and their color depends on the strength of the shocks and how long ago they occurred:

Information on the site is updated every minute (!), so you get the most relevant and fresh information about seismic activity on Earth.

The epicenters have a different color depending on the strength of the shocks (green - up to three, burgundy - over six):

The left part of the window displays a feed of seismic events in the world (the most recent ones are at the top). By clicking on any of them, you will move to the desired point on the world map and see the details in a pop-up window:

Everything is fine, the animation is cool and interesting, makes big picture more visual, but it is because of it that the site noticeably slows down. Maybe it's just me (if you haven't had any problems with it - unsubscribe in the comments).
A low howling sound was heard from under the ground, then repeated and began to grow. Instinctive fear made me jump to my feet. At that moment, the ground beneath me trembled. There was a palpable jolt from below. Then it shook so that I fell on my side. It creaked under the ground. Suddenly, a winding crack split the dune and immediately disappeared, swallowed up by crumbling sand. The murmur, which had subsided, began to grow again. Again, the push is stronger than those that have already been. The hum and rattle were deafening. The dune was leaving me: sand, like water, flowed down. All of a sudden everything was quiet. The aftershocks have stopped
Nedyalkov, 1970
Earthquakes do not occur everywhere on Earth. In some parts of the world they occur frequently, while in others they almost never occur. If you look at the map of our planet, on which the centers of seismic activity are plotted, then it is easy to notice the quirkiness of the resulting “pattern”. Scientists began to unravel this pattern when they became convinced that the earth's crust is not a single monolith. Basically, earthquake sources are concentrated in three zones:
The first zone is the Pacific belt. It covers the coast of Alaska, Kamchatka, the western coast of the North and South America, then stretches to Australia, passes through Indochina, the coast of China and captures JapanThe second zone is the Mediterranean-Asian belt. It runs in a wide strip from Portugal and Spain through Italy, Balkan Peninsula, Iran, the Caucasus, the countries of Southwest Asia, through the Central Asian republics, goes to the Baikal region and then connects to the Pacific coast with the first belt
The third zone runs along the median ridges in the Atlantic and Indian Oceans, where giant seismically active zones are located. The ridges are connected to each other, and the median ridge indian ocean bypasses Australia from the south and connects with another ridge - the East Pacific Rise. It stretches east to Central America and then to the Gulf of California. The entire system of ridges is characterized by a turbulent geological situation. Volcanoes often erupt here, and earthquakes form a whole series: many hundreds of shocks occur on small area for a short time
Of the three seismic zones, the most active is the Pacific coast and its islands. Suffice it to say that of all the annually released the globe during earthquakes, energy in the amount of 10.25 to 10.26 erg (corresponds approximately to the energy of the Dneproges power plant with continuous operation for 300-350 years), the Pacific belt accounts for 75-80%. 2/3 of the world's largest earthquakes occur here
In the Mediterranean-Asian belt (it is often called the Alpine) total number earthquakes are somewhat less: their total energy is 15-20% of the world's seismic energy. Compared to the Pacific and Alpine belts, the seismic activity of the mid-ocean ridges is low. Earthquakes are not so strong here (3-7% of the seismic energy of all earthquakes in the world)
The Krasnoyarsk Territory is a seismically relatively calm zone, however, in our time, tremors occur more often and become stronger
On Earth, there are special zones of increased seismic activity, where earthquakes constantly occur. Why is this happening? Why do earthquakes occur more often in mountainous areas and very rarely in deserts? Why in pacific ocean earthquakes happen all the time, generating tsunamis of varying degrees of danger, but we have heard almost nothing about earthquakes in the Arctic Ocean. It's all about the seismic belts of the earth.
The seismic belts of the earth are the places where the lithospheric plates of the planet come into contact with each other. In these zones, where the seismic belts of the Earth are formed, there is an increased mobility of the earth's crust, volcanic activity, due to the process of mountain building, which lasts for millennia.
The length of these belts is incredibly large - the belts stretch for thousands of kilometers.
There are two large seismic belts on the planet: the Mediterranean-Trans-Asian and the Pacific.

Rice. 1. Seismic belts of the Earth.
Mediterranean-Trans-Asian the belt originates off the coast of the Persian Gulf and ends in the middle Atlantic Ocean. This belt is also called the latitudinal belt, as it stretches parallel to the equator.
TOP 1 articlewho read along with this
pacific belt- meridional, it stretches perpendicular to the Mediterranean-Trans-Asian belt. It is on the line of this belt that great amount active volcanoes, most of the eruptions of which occur under the water column of the Pacific Ocean itself.
If you draw the seismic belts of the Earth on contour map- you get an interesting and mysterious picture. The belts seem to border the ancient platforms of the Earth, and sometimes they are embedded in them. They are associated with giant faults in the earth's crust, both ancient and younger.
The latitudinal seismic belt of the Earth passes through the Mediterranean Sea and all the European mountain ranges adjacent to it, located in the south of the continent. It stretches through the mountains of Asia Minor and North Africa, reaches the mountain ranges of the Caucasus and Iran, runs through the entire Central Asia and the Hindu Kush straight to Koel Lun and the Himalayas.
In this belt, the most active seismic zones are the Carpathian Mountains located on the territory of Romania, all of Iran and Balochistan. From Balochistan, the earthquake zone extends to Burma.

Fig.2. Mediterranean-Trans-Asian seismic belt
This belt has active seismic zones, which are located not only on land, but also in the waters of two oceans: the Atlantic and Indian. Partially, this belt captures the Arctic Ocean. The seismic zone of the entire Atlantic passes through the Greenland Sea and Spain.
The most active seismic zone of the latitudinal belt falls on the bottom of the Indian Ocean, passes through the Arabian Peninsula and stretches to the very south and southwest of Antarctica.
But, no matter how dangerous the latitudinal seismic belt is, nevertheless, most of all earthquakes (about 80%) that occur on our planet occur in the Pacific belt of seismic activity. This belt runs along the bottom of the Pacific Ocean, along all mountain ranges encircling this very big ocean Land, captures the islands located in it, including Indonesia.

Fig.3. Pacific seismic belt.
The largest part of this belt is the Eastern. It originates in Kamchatka, stretches through the Aleutian Islands and western coastal zones North and South America straight to the South Antilles loop.
The eastern branch is unpredictable and poorly understood. It is full of sharp and twisty turns.
The northern part of the belt is the most seismically active, which is constantly felt by the inhabitants of California, as well as Central and South America.
The western part of the meridional belt originates in Kamchatka, stretches to Japan and beyond.
It is no secret that during earthquakes, waves from vibrations of the earth's crust can reach remote areas that are considered safe in relation to seismic activity. In some places, the echoes of earthquakes are not felt at all, and in some they reach several points on the Richter scale.

Fig.4. Earth seismic activity map.
Basically, these zones, sensitive to fluctuations of the earth's crust, are located under the water column of the oceans. The secondary seismic belts of the planet are located in the waters of the Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Indian Ocean and in the Arctic. Most of secondary belts fall on the eastern part of the planet, so these belts stretch from the Philippines, gradually descending to Antarctica. Echoes of shocks can still be felt in the Pacific Ocean, but in the Atlantic it is almost always a seismically calm zone.
So, on Earth, earthquakes do not occur in random places. It is possible to predict the seismic activity of the earth's crust, since the main part of earthquakes occurs in special zones, which are called the seismic belts of the earth. There are only two of them on our planet: the latitudinal Mediterranean-Trans-Asian seismic belt, which stretches parallel to the Equator, and the meridional Pacific seismic belt, located perpendicular to the latitudinal one.
Average rating: 4.1. Total ratings received: 494.